Spring Cloud - Openfeign 实现原理分析
OpenFeign简介
OpenFeign 是一个声明式 RESTful 网络请求客户端。OpenFeign 会根据带有注解的函数信息构建出网络请求的模板,在发送网络请求之前,OpenFeign 会将函数的参数值设置到这些请求模板中。虽然 OpenFeign 只能支持基于文本的网络请求,但是它可以极大简化网络请求的实现,方便编程人员快速构建自己的网络请求应用。
核心组件与概念
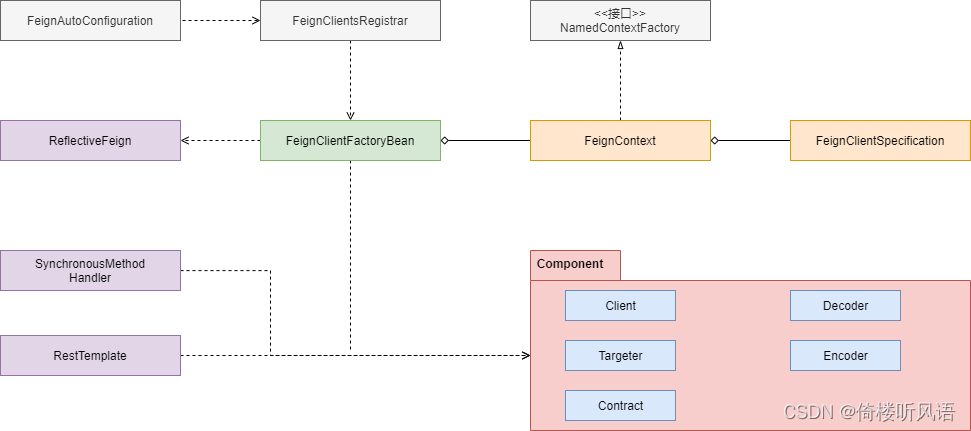
在阅读源码时,可以沿着两条线路进行,一是被@FeignClient注解修饰的接口类如何创建,也就是其 Bean 实例是如何被创建的;二是调用这些接口类的网络请求相关函数时,OpenFeign 是如何发送网络请求的。而 OpenFeign 相关的类也可以以此来进行分类,一部分是用来初始化相应的 Bean 实例的,一部分是用来在调用方法时发送网络请求。
动态注册BeanDefinition
1. FeignClientsRegistrar
@EnableFeignClients 有三个作用,一是引入FeignClientsRegistrar;二是指定扫描FeignClient的包信息,就是指定FeignClient接口类所在的包名;三是指定FeignClient接口类的自定义配置类。@EnableFeignClients注解的定义如下所示:
public @interface EnableFeignClients {
// 下面三个函数都是为了指定需要扫描的包
String[] value() default {};
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
// 指定自定义feign client的自定义配置,可以配置 Decoder、Encoder和Contract等组件
// FeignClientsConfiguration 是默认的配置类
Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {};
// 指定被@FeignClient修饰的类,如果不为空,那么路径自动检测机制会被关闭
Class<?>[] clients() default {};
}
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClientsRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 从 EnableFeignClients 的属性值来构建 Feign 的自定义 Configuration 进行注册
registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry);
// 扫描 package , 注册被 @FeignClient 修饰的接口类的Bean信息
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
private void registerClientConfiguration(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object name,
Object configuration) {
// 使用 BeanDefinitionBuilder 来生成 BeanDefinition, 并注册到 registry 上
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientSpecification.class);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(name);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(configuration);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(
name + "." + FeignClientSpecification.class.getSimpleName(),
builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
FeignClientSpecification 类实现了 NamedContextFactory.Specification 接口,它是 OpenFeign 组件实例化的重要一环,它持有自定义配置类提供的组件实例,供 OpenFeign 使用。SpringCloud 框架使用 NamedContextFactory 创建一系列的运行上下文,来让对应的 Specification 在这些上下文中创建实例对象。
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignAutoConfiguration
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<FeignClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
public FeignContext feignContext() {
// 创建 FeignContext 实例, 并将 FeignClientSpecification 注入
FeignContext context = new FeignContext();
context.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return context;
}
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignContext#FeignContext
public FeignContext() {
// 将默认的 FeignClientsConfiguration 作为参数传递给构造函数
super(FeignClientsConfiguration.class, "feign", "feign.client.name");
}
NamedContextFactory 是 FeignContext 的父类, 其 createContext 方法会创建具有名称为 Spring 的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 实例作为当前上下文的子上下文。这些 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 实例可以管理 OpenFeign 组件的不同实例。
NamedContextFactory 的实现代码如下:
// org.springframework.cloud.context.named.NamedContextFactory#createContext
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 获取该 name 所对应的 configuration ,如果有的话,就注册到子 context 中
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name).getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
// 注册 default 的 Configuration, 也就是 FeignClientsRegistrar 类的 registerDefaultConfiguration 方法中注册的Configuration
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
// 注册 PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration 和 FeignClientsConfiguration 配置类
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class, this.defaultConfigType);
// 设置子 context 的 Environment 的 propertySource 属性源
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(
this.propertySourceName,
Collections.<String, Object>singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
// 所有 context 的 parent 都相同,这样的话,一些相同的Bean可以通过 parent context 来获取
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
// jdk11 issue
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/3101
context.setClassLoader(this.parent.getClassLoader());
}
context.setDisplayName(generateDisplayName(name));
context.refresh();
return context;
}
2. 扫描类信息
FeignClientsRegistrar 做的第二件事情是扫描指定包下的类文件,注册 @FeignClient 注解修饰的接口类信息。
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClientsRegistrar#registerFeignClients
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 自定义扫描类
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = getScanner();
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
Set<String> basePackages;
// 获取 EnableFeignClients 配置信息
Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName());
// 依照 Annotation 来进行 TypeFilter ,只会扫描出被 FeignClient 修饰的类
AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter(FeignClient.class);
final Class<?>[] clients = attrs == null ? null : (Class<?>[]) attrs.get("clients");
// 如果没有配置 clients 属性,那么需要扫描 basePackage,所以设置了 AnnotationTypeFilter, 并且去获取 basePackage
if (clients == null || clients.length == 0) {
scanner.addIncludeFilter(annotationTypeFilter);
basePackages = getBasePackages(metadata);
}
else {
final Set<String> clientClasses = new HashSet<>();
basePackages = new HashSet<>();
for (Class<?> clazz : clients) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
clientClasses.add(clazz.getCanonicalName());
}
AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter filter = new AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter() {
@Override
protected boolean match(ClassMetadata metadata) {
String cleaned = metadata.getClassName().replaceAll("\\$", ".");
return clientClasses.contains(cleaned);
}
};
scanner.addIncludeFilter(
new AllTypeFilter(Arrays.asList(filter, annotationTypeFilter)));
}
// 遍历上述过程中获取的 basePackages 列表
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidateComponents = scanner
.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) {
if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent;
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(),
"@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface");
// 从这些 BeanDefinitaion 中获取FeignClient的属性值
Map<String, Object> attributes = annotationMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName());
String name = getClientName(attributes);
// 对单独某个 FeignClient 的 configuration 进行配置
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,attributes.get("configuration"));
// 注册 FeignClient 的 BeanDefinition
registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}
实例初始化
FeignClientFactoryBean 是工厂类, Spring 窗口通过调用它的 getObject 方法来获取对应的 Bean 实例。 被 @FeignClient 修饰的接口类都是通过 FeignClientFactoryBean 的 getObject 方法进行实例化的,具体实现如下代码所示:
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClientFactoryBean
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return getTarget();
}
/**
* @param <T> the target type of the Feign client
* @return a {@link Feign} client created with the specified data and the context
* information
*/
<T> T getTarget() {
FeignContext context = this.applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
this.url = this.name;
}
this.url += cleanPath();
return (T) loadBalance(builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, this.url));
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.url;
}
String url = this.url + cleanPath();
// 调用 FeignContext的 getInstance 方法获取Client对象
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
// 因为有具体的url,所以就不需要负载均衡,所以除去 LoadBalancerFeignClient 实例
if (client != null) {
if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient) client).getDelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
}
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, url));
}
这里就用到了 FeignContext 的 getInstance 方法
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
if (BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context,
type).length > 0) {
// 从对应的 context 中获取 Bean 实例,如果对应的子上下文没有则直接从父上下文中获取
return context.getBean(type);
}
return null;
}
在 Feign.Builder 中会构建几个重要组件
protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) {
FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class);
Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(this.type);
// @formatter:off
Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class)
// required values
.logger(logger)
.encoder(get(context, Encoder.class))
.decoder(get(context, Decoder.class))
.contract(get(context, Contract.class));
// @formatter:on
configureFeign(context, builder);
return builder;
}
Feign.Builder 负责生成被 @FeignClient 修饰的 FeignClient 接口类实例。它通过 Java 反射机制,构造 InvocationHandler 实例并将其注册到 FeignClient 上,当 FeignClient 的方法被调用时, InvocationHandler 的回调函数会被调用, OpenFeign 会在其回调函数中发送网络请求。build 方法如下:
// feign.Feign.Builder#build
public Feign build() {
SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory synchronousMethodHandlerFactory =
new SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory(client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger,
logLevel, decode404, closeAfterDecode, propagationPolicy);
ParseHandlersByName handlersByName =
new ParseHandlersByName(contract, options, encoder, decoder, queryMapEncoder,
errorDecoder, synchronousMethodHandlerFactory);
return new ReflectiveFeign(handlersByName, invocationHandlerFactory, queryMapEncoder);
}
}
ReflectiveFeign 的 newInstance 方法是生成 FeignClient 实例的关键实现。它主要做了两件事情,一是扫描 FeignClient 接口类的所有函数,生成对应的 Hander ;二是使用 Proxy生成 FeignClient 的实例对象,代码如下所示:
// feign.ReflectiveFeign#newInstance
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
} else if (Util.isDefault(method)) {
// 为每个默认方法生成一个 DefaultMethodHandler
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
// 生成 java reflective 的 InvocationHandler
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] {target.type()}, handler);
// 将 defaluMethodHandler 绑定到 proxy 中
for (DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
1. 扫描函数信息
在扫描 FeignClient 接口类所有的函数生成对应的 Handler 的过程中,OpenFeing 会生成调用该函数时发送网络请求的模板,也就是 RestTemplate 实例。ParseHandlersByName 的 apply 方法就是这一过程的具体实现。
public Map<String, MethodHandler> apply(Target key) {
// 获取 type 的所有方法信息,会根据注解生成每个方法的 ResquestTemplate
List<MethodMetadata> metadata = contract.parseAndValidatateMetadata(key.type());
Map<String, MethodHandler> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, MethodHandler>();
for (MethodMetadata md : metadata) {
BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs buildTemplate;
if (!md.formParams().isEmpty() && md.template().bodyTemplate() == null) {
buildTemplate = new BuildFormEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder, queryMapEncoder);
} else if (md.bodyIndex() != null) {
buildTemplate = new BuildEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder, queryMapEncoder);
} else {
buildTemplate = new BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs(md, queryMapEncoder);
}
result.put(md.configKey(),
factory.create(key, md, buildTemplate, options, decoder, errorDecoder));
}
return result;
}
}
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.support.SpringMvcContract#parseAndValidateMetadata
public MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method) {
this.processedMethods.put(Feign.configKey(targetType, method), method);
// 调用父类方法
MethodMetadata md = super.parseAndValidateMetadata(targetType, method);
// 处理 RequestMapping 注解
RequestMapping classAnnotation = findMergedAnnotation(targetType,RequestMapping.class);
if (classAnnotation != null) {
// produces - use from class annotation only if method has not specified this
if (!md.template().headers().containsKey(ACCEPT)) {
parseProduces(md, method, classAnnotation);
}
// consumes -- use from class annotation only if method has not specified this
if (!md.template().headers().containsKey(CONTENT_TYPE)) {
parseConsumes(md, method, classAnnotation);
}
// headers -- class annotation is inherited to methods, always write these if
// present
parseHeaders(md, method, classAnnotation);
}
return md;
}
// feign.Contract.BaseContract#parseAndValidateMetadata
protected MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method) {
MethodMetadata data = new MethodMetadata();
// 函数的返回值
data.returnType(Types.resolve(targetType, targetType, method.getGenericReturnType()));
data.configKey(Feign.configKey(targetType, method));
// 获取并处理 class 的注解信息
if (targetType.getInterfaces().length == 1) {
processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType.getInterfaces()[0]);
}
processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType);
// 处理修饰 method 的注解信息
for (Annotation methodAnnotation : method.getAnnotations()) {
processAnnotationOnMethod(data, methodAnnotation, method);
}
checkState(data.template().method() != null,
"Method %s not annotated with HTTP method type (ex. GET, POST)",
method.getName());
// 函数参数类型
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
// 函数注解类型
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
int count = parameterAnnotations.length;
// 依次处理各个函数参数注解
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
boolean isHttpAnnotation = false;
if (parameterAnnotations[i] != null) {
// 处理参数的注解,并且返回该参数来指明是否为将要发送请求的 body 。除了 body 之处,还可能是 path , param 等
isHttpAnnotation = processAnnotationsOnParameter(data, parameterAnnotations[i], i);
}
if (parameterTypes[i] == URI.class) {
data.urlIndex(i);
} else if (!isHttpAnnotation) {
checkState(data.formParams().isEmpty(),
"Body parameters cannot be used with form parameters.");
checkState(data.bodyIndex() == null, "Method has too many Body parameters: %s", method);
// 表明发送请求 body 的参数位置和参数类型
data.bodyIndex(i);
data.bodyType(Types.resolve(targetType, targetType, genericParameterTypes[i]));
}
}
if (data.headerMapIndex() != null) {
checkMapString("HeaderMap", parameterTypes[data.headerMapIndex()],
genericParameterTypes[data.headerMapIndex()]);
}
if (data.queryMapIndex() != null) {
if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[data.queryMapIndex()])) {
checkMapKeys("QueryMap", genericParameterTypes[data.queryMapIndex()]);
}
}
return data;
}
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.support.SpringMvcContract#processAnnotationOnClass
protected void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<?> clz) {
if (clz.getInterfaces().length == 0) {
// 获取 RequestMapping 的注解信息,并设置 MethodMetadata.template 的数据
RequestMapping classAnnotation = findMergedAnnotation(clz,
RequestMapping.class);
if (classAnnotation != null) {
// Prepend path from class annotation if specified
if (classAnnotation.value().length > 0) {
String pathValue = emptyToNull(classAnnotation.value()[0]);
pathValue = resolve(pathValue);
if (!pathValue.startsWith("/")) {
pathValue = "/" + pathValue;
}
data.template().uri(pathValue);
}
}
}
}
processAnnotationOnMethod 方法的主要作用是处理修饰函数的注解。
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.support.SpringMvcContract#processAnnotationOnMethod
protected void processAnnotationOnMethod(MethodMetadata data,
Annotation methodAnnotation, Method method) {
if (!RequestMapping.class.isInstance(methodAnnotation) && !methodAnnotation
.annotationType().isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
return;
}
RequestMapping methodMapping = findMergedAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
// HTTP Method
// 处理 HTTP method
RequestMethod[] methods = methodMapping.method();
if (methods.length == 0) {
// 默认是get
methods = new RequestMethod[] { RequestMethod.GET };
}
checkOne(method, methods, "method");
data.template().method(Request.HttpMethod.valueOf(methods[0].name()));
// path
// 处理请求路径
checkAtMostOne(method, methodMapping.value(), "value");
if (methodMapping.value().length > 0) {
String pathValue = emptyToNull(methodMapping.value()[0]);
if (pathValue != null) {
pathValue = resolve(pathValue);
// Append path from @RequestMapping if value is present on method
if (!pathValue.startsWith("/") && !data.template().path().endsWith("/")) {
pathValue = "/" + pathValue;
}
data.template().uri(pathValue, true);
}
}
// 处理生产
// produces
parseProduces(data, method, methodMapping);
// 处理消费
// consumes
parseConsumes(data, method, methodMapping);
// 处理头部
// headers
parseHeaders(data, method, methodMapping);
data.indexToExpander(new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Param.Expander>());
}
而 processAnnotationsOnParameter 方法则主要处理修饰函数参数的注解。它会根据注解类型来调用不同的 AnnotatedParameterProcessor 的实现类,解析注解的属性信息。函数参数的注解类型包括: @RequestParam、@RequestHeader和@PathVariable。 processAnnotationsOnParameter 方法的具体实现如下代码所示:
// org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.support.SpringMvcContract#processAnnotationsOnParameter
protected boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data,
Annotation[] annotations, int paramIndex) {
boolean isHttpAnnotation = false;
AnnotatedParameterProcessor.AnnotatedParameterContext context = new SimpleAnnotatedParameterContext(
data, paramIndex);
Method method = this.processedMethods.get(data.configKey());
// 遍历所有的参数注解
for (Annotation parameterAnnotation : annotations) {
// 不同的注解类型有不同的 Processor
AnnotatedParameterProcessor processor = this.annotatedArgumentProcessors
.get(parameterAnnotation.annotationType());
if (processor != null) {
// 合成@AliasFor注解并处理
Annotation processParameterAnnotation;
// synthesize, handling @AliasFor, while falling back to parameter name on
// missing String #value():
processParameterAnnotation = synthesizeWithMethodParameterNameAsFallbackValue(
parameterAnnotation, method, paramIndex);
isHttpAnnotation |= processor.processArgument(context,
processParameterAnnotation, method);
}
}
if (isHttpAnnotation && data.indexToExpander().get(paramIndex) == null) {
TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor = createTypeDescriptor(method, paramIndex);
if (this.conversionService.canConvert(typeDescriptor,
STRING_TYPE_DESCRIPTOR)) {
Param.Expander expander = this.convertingExpanderFactory
.getExpander(typeDescriptor);
if (expander != null) {
data.indexToExpander().put(paramIndex, expander);
}
}
}
return isHttpAnnotation;
}
AnnotatedParameterProcessor 是一个接口,有四个实现类: PathVariableParameterProcessor、RequestHeaderParameterProcessor、RequestParamParameterProcessor、QueryMapParameterProcessor,四者分別用于處理 @PathVariable、@RequestHeader、@RequestParam和@SpringQueryMap.
ParseHandlersByName 的 apply 方法通过 Contract 的 parseAndValidatateMetadata 方法获得了接口类中所有方法的元数据,这些信息中包含了每个方法所对应的网络请求信息。
// feign.SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory#create
public MethodHandler create(Target<?> target,
MethodMetadata md,
RequestTemplate.Factory buildTemplateFromArgs,
Options options,
Decoder decoder,
ErrorDecoder errorDecoder) {
return new SynchronousMethodHandler(target, client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger,
logLevel, md, buildTemplateFromArgs, options, decoder,
errorDecoder, decode404, closeAfterDecode, propagationPolicy);
}
2. 生成Proxy接口类
生成相应接口类的实例对象
// feign.ReflectiveFeign#newInstance
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] {target.type()}, handler);
// 将 defaultMethodHandler 绑定到 proxy
for (DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
// feign.InvocationHandlerFactory.Default
static final class Default implements InvocationHandlerFactory {
@Override
public InvocationHandler create(Target target, Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch) {
return new ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler(target, dispatch);
}
}
ReflectiveFeign
// feign.ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler#invoke
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
Object otherHandler =
args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0]) : null;
return equals(otherHandler);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
return false;
}
} else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) {
return hashCode();
} else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) {
return toString();
}
return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
}
函数调用和网络请求
在配置和实例生成结束之后,就可以直接使用 FeignClient 接口类的实例,调用它的函数来发送网络请求。由于是代理类,所以最终函数会执行 SynchronousMethodHandler 的 invoke 方法。在该方法中,OpenFeign 会将函数的实际参数值与之前生成的 RequestTemplate 进行结合,然后发送网络请求。
// feign.SynchronousMethodHandler#invoke
public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {
// 根据函数参数创建 RequestTemplate 实例, buildTemplateFromArgs 是 RequestTemplate.Factory 接口的实例
RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv);
Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone();
while (true) {
try {
return executeAndDecode(template);
} catch (RetryableException e) {
try {
retryer.continueOrPropagate(e);
} catch (RetryableException th) {
Throwable cause = th.getCause();
if (propagationPolicy == UNWRAP && cause != null) {
throw cause;
} else {
throw th;
}
}
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel);
}
continue;
}
}
}
// feign.ReflectiveFeign.BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs#create
public RequestTemplate create(Object[] argv) {
RequestTemplate mutable = RequestTemplate.from(metadata.template());
if (metadata.urlIndex() != null) {
int urlIndex = metadata.urlIndex();
checkArgument(argv[urlIndex] != null, "URI parameter %s was null", urlIndex);
mutable.target(String.valueOf(argv[urlIndex]));
}
Map<String, Object> varBuilder = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
// 遍历 MethodMetadata 中所有关于参数的索引及其对应名称的配置信息
for (Entry<Integer, Collection<String>> entry : metadata.indexToName().entrySet()) {
int i = entry.getKey();
Object value = argv[entry.getKey()];
if (value != null) { // Null values are skipped.
if (indexToExpander.containsKey(i)) {
value = expandElements(indexToExpander.get(i), value);
}
for (String name : entry.getValue()) {
varBuilder.put(name, value);
}
}
}
RequestTemplate template = resolve(argv, mutable, varBuilder);
if (metadata.queryMapIndex() != null) {
// add query map parameters after initial resolve so that they take
// precedence over any predefined values
Object value = argv[metadata.queryMapIndex()];
// 设置 queryMap 参数
Map<String, Object> queryMap = toQueryMap(value);
template = addQueryMapQueryParameters(queryMap, template);
}
// 设置 headersMap 参数
if (metadata.headerMapIndex() != null) {
template =
addHeaderMapHeaders((Map<String, Object>) argv[metadata.headerMapIndex()], template);
}
return template;
}
executeAndDecode 方法根据 template 生成 Request 对象
// feign.SynchronousMethodHandler#executeAndDecode
Object executeAndDecode(RequestTemplate template) throws Throwable {
Request request = targetRequest(template);
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRequest(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, request);
}
Response response;
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
response = client.execute(request, options);
} catch (IOException e) {
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logIOException(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, e, elapsedTime(start));
}
throw errorExecuting(request, e);
}
long elapsedTime = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - start);
boolean shouldClose = true;
try {
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
response =
logger.logAndRebufferResponse(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, response, elapsedTime);
}
// 如果返回值类型是 Response 则直接返回
if (Response.class == metadata.returnType()) {
if (response.body() == null) {
return response;
}
if (response.body().length() == null ||
response.body().length() > MAX_RESPONSE_BUFFER_SIZE) {
shouldClose = false;
return response;
}
// Ensure the response body is disconnected
byte[] bodyData = Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream());
return response.toBuilder().body(bodyData).build();
}
if (response.status() >= 200 && response.status() < 300) {
if (void.class == metadata.returnType()) {
return null;
} else {
Object result = decode(response);
shouldClose = closeAfterDecode;
return result;
}
} else if (decode404 && response.status() == 404 && void.class != metadata.returnType()) {
Object result = decode(response);
shouldClose = closeAfterDecode;
return result;
} else {
throw errorDecoder.decode(metadata.configKey(), response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logIOException(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, e, elapsedTime);
}
throw errorReading(request, response, e);
} finally {
if (shouldClose) {
ensureClosed(response.body());
}
}
}
OpenFeign 也提供了 RequestInterceptory 机制, 在由 RequestTemplate 生成 Request 的过程中,会调用所有 RequestInteceptor 对 RequestTemplate 进行处理。
// feign.SynchronousMethodHandler#targetRequest
Request targetRequest(RequestTemplate template) {
for (RequestInterceptor interceptor : requestInterceptors) {
interceptor.apply(template);
}
return target.apply(template);
}